Leads4pass 300-410 Dumps Exam Solution Updated!
Comprehensive upgrade of CCNP Enterprise 300-410 exam materials:
- Verify actual scenarios and make corrections and re-edits.
- Multiple verifications ensure more than 90% effectiveness.
- Offering 2025 Newest Simulation Labs
- Added multiple test question types
In summary! Leads4pass has fully updated the exam materials for the latest CCNP Enterprise 300-410 exam and launched 925 latest exam questions and answers to ensure you pass the exam 100% successfully.
Leads4pass 300-410 dumps details
| Total Questions: | 925 |
| Single & Multiple Choice: | 891 |
| Drag Drop: | 24 |
| Simulation Labs: | 10 |
| Last Updated: | Jan 11, 2025 |
Download Leads4pass 300-410 dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html, Use PDF or VCE tools to help you easily complete the target practice plan.
Online practice New 300-410 dumps exam materials:
| From | Number of exam questions | Price | Associated certifications | Exam details |
| Leads4pass | 15/925 | Free | CCNP Enterprise | 300-410 exam topics |
New Question 1:
Refer to the exhibit. R1 is configured with IP SLA to check the availability of the server behind R6 but it kept failing. Which configuration resolves the issue?

A. R1(config)# ip sla 700 R1(config-track)# delay down 30 up 20
B. R1(config)# ip sla 700 R1(config-track)# delay down 20 up 30
C. R1(config)# track 700 ip sla 700 R1(config-track)# delay down 30 up 20
D. R1(config)# track 700 ip sla 700 R1(config-track)# delay down 20 up 30
Correct Answer: C
New Question 2:
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator logs into the router using TACACS+ username and password credentials, but the administrator cannot run any privileged commands

Which action resolves the issue?
A. Configure TACACS+ synchronization with the Active Directory admin group
B. Configure the username from a local database
C. Configure full access for the username from TACACS+ server
D. Configure an authorized IP address for this user to access this router
Correct Answer: C
New Question 3:
You have implemented an automatic 6-to-4 tunnel between the routers rtrA and rtrB as shown in the following network diagram:

The routers rtrA and rtrB are connected to two IPv6 subnets and are separated by an IPv4 network. You decide to verify whether the tunnel was correctly implemented using the show running-config command. Which of the following commands should exist in the output of the show running-config command on rtrA and rtrB? (Choose all that apply.)
A. interface tunnel
B. tunnel source
C. tunnel destination
D. tunnel mode ipv6ip
E. tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4
Correct Answer: ABE
The following commands should exist in the output of the show running-config command on rtrA and rtrB: interface tunnel tunnel source tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4
The interface tunnel command is used to define a tunnel interface on the router. The tunnel source command allows you to specify the source of the tunnel, which is the router interface that faces the IPv4 network. The tunnel source must be configured with an IPv4 address. The tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4 command is used to specify the tunneling mechanism, which in this case is automatic 6-to-4.
The partial output of the show running-config command on rtrA is as follows:
!
interface Tunnel0
no ip address
tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4
tunnel source 172.50.20.5
ipv6 address 2002:ac32:of06::1/48
!
The partial output of the show running-config command on rtrB is as follows:
!
interface Tunnel0
no ip address
tunnel mode ipv6ip 6to4
tunnel source 172.50.20.1
ipv6 address 2002:ac32:0f06::2/48
!
The tunnel destination command and the tunnel mode ipv6ip commands do not appear in the show running- config output when automatic 6-to-4 tunnels are implemented on rtrA and rtrB. Both of these commands are executed for manually configured tunnels.
Objective:
Network Principles
Sub-Objective:
Recognize proposed changes to the network
References:
Cisco Press > Articles > Cisco Certification > CCNP > CCNP Self-Study: Advanced IP Addressing Cisco Interface and Hardware Component Configuration Guide > IPv6 Automatic 6to4 Tunnels Cisco > Support > Technology Support > IP >
IP Version 6 (IPV6) > Configure > Configuration Examples and Technotes > IPv6 Tunnel Through an IPv4 Network
Cisco IOS IPv6 Implementation Guide > Implementing Tunneling for IPv6
New Question 4:
Examine the following FIB table:

Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A. These are the default entries in an FIB table
B. No IP addresses have been configured on this router
C. Multicast routing is enabled
D. The gateway of last resort has not been set
Correct Answer: C
The Forwarding Information Base (FIB) table is created when Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) is enabled on the router. FIB is a mapping of destination networks and IP addresses to next-hop IP addresses and exit interfaces.
In the scenario, multicast routing has NOT enabled in the router. If it were enabled, the next hop for the 224.0.0.0/4 network would not be listed as drop. A drop means any packets sent to multicast IP addresses will be dropped.
If multicast routing were enabled, the entry for 224.0.0.0 would appear as follows:
Prefix Next Hop Interface
224.0.0.0/4 0.0.0.0
The next hop of 0.0.0.0 means that this traffic will be process switched, and CEF cannot forward the packets.
The table displayed in the scenario contains the default entries in the FIB. These entries will change based on further configuration of the router interfaces and the addition of routes to the routing table through either static routing or through routing protocols.
No IP addresses have been configured on the router. Had they been configured, the addresses of the networks to which they were connected would be in the table. For example, if the IP address of the FastEthernet 0/1 interface were set to 192.168.1.1/24, three entries would have been added to the table as follows:

While the first IP address represents the directly attached network of which the interface is a member, the second IP address represents the network ID of the network, the third IP address represents the specific IP address assigned to the interface, and the last IP address represents the broadcast address of the network.
The gateway of last resort has not been set on the router. If it were set, it would be listed along with an IP address for the next hop and the exit interface. An entry for a gateway of last resort (or default route) would resemble the following:
Prefix Next Hop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 192.168.5.5 FastEthernet 0/0
Objective:
Network Principles
Sub-Objective:
Identify Cisco Express Forwarding concepts
References:
Cisco IOS Switching Services Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 > Cisco Express Forwarding Overview Cisco > Home > Support > Product Support > Routers > Cisco 12000 Series Routers > Troubleshoot and Alerts > Troubleshooting
Technotes > Understanding Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) https://www.ccexpert.us/traffic-share/fib-entries.html
New Question 5:
Which of the following IPv6 addresses correctly represent the shortened version of the IP address 2031:0000:0000:130F:0000:0000:876A:130B? (Choose two.)
A. 2031::130F::876A:130B
B. 2031::130F:0:0:876A:130B
C. 2031:0:130F::876A:130B
D. 2031:0:0:130F::876A:130B
Correct Answer: BD
2031:0000:0000:130F:0000:0000:876A:130B can be shortened to either 2031::130F:0:0:876A:130B or 2031:0:0:130F::876A:130B.
IPv6 addresses are written in 16-bit hexadecimal number fields separated by a colon (:). There are a total of eight 16-bit fields, making each IPv6 address a total of 128 bits. The hexadecimal letters are NOT case sensitive.
You can shorten an IPv6 address by removing the leading zeros in any address field. You can only remove zeros that are the first character in an address field. For example, FFC0:02C0: is the same as FFC0:2C0:.
However, FFC0:8020 is not the same as FFC0:802:.
If a 16-bit address field contains all zeros, then it can be represented by a single zero. For example, FF80:0000: is the same as FF80:0:.
You can use double colons (::) to represent successive address fields of zeros. An address parser can determine the number of missing fields and then insert the proper number of zeros to complete the address. For example,
FF80:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001 is the same as FF80::1, and 0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001 could be written as ::1. However, you can only have one set of double colons (::) in an address; therefore,
FF80:0000:0000:0CB0:0000:0000:0000:0001 cannot be written as F80::0CB0::1.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Identify IPv6 addressing and subnetting
References:
Cisco > IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity Configuration Guide > IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity
Cisco > IPv6 Addressing at a Glance (PDF)
New Question 6:
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer implemented an access list on R1 to allow anyone to Telnet except R2 Loopback0 to R1 Loopback4 How must sequence 20 be replaced on the R1 access list to resolve the issue?
A. sequence 20 permit tcp host 1001:ABC:2011:7::1 host 400A:0:400C::1 eq telnet
B. sequence 20 deny tcp host 400A:0:400C::1 host 1001:ABC:2011:7::1 eq telnet
C. sequence 20 permit tcp host 400A:0:400C::1 host 1001:ABC:2011:7::1 eq telnet
D. sequence 20 deny tcp host 1001:ABC:2011:7::1 host 400A:0:400C::1 eq telnet
Correct Answer: D
New Question 7:
Consider the partial output of the show ip bgp command:

Which of the following statements are TRUE about the given output? (Choose all that apply.)
A. The 10.62.7.0 route is learned by the router through an iBGP neighbor.
B. All five routes have been originated by an IGP.
C. The router is aware of the best path for the 61.80.3.0 destination.
D. There are four AS between the router and the 192.177.1.0 subnet.
Correct Answer: AB
The following statements are TRUE about the given output:
The 10.62.7.0 route is learned by the router through an iBGP neighbor.
All five routes have been originated by an IGP.
The show ip bgp command displays information about the BGP routing table, including origin type, metric, next-hop addresses for every route learned by BGP, router ID, local preference, and BGP path. In the output, the character i in the first entry of the 10.62.7.0 destination indicates that the route was learned by an iBGP neighbor.
The * symbol at the beginning of the routes indicate that they are valid routes, while the > symbol indicate that the route is the current best route.
The i at the end of the entries under the Path column indicates that the routes have been originated by an interior gateway protocol (IGP). In the scenario output, all five routes have an i at the end of their respective entries.
If the character appears as the origin code, the routes are considered to have originated from an exterior gateway protocol (EGP). The origin code can also be the ? character, which implies that the origin of the route is unknown.
The output also displays the next-hop addresses for the routes. The 200.7.34.0 subnet is a local route, and hence has its next-hop address as 0.0.0.0.
The show ip bgp command also displays the local router\’s ID (RID), local preference, weight, and next-hop addresses for every route learned by BGP. In this case, the RID of RouterA is 200.17.34.15 and the local preference, weight, and next-hop address for the 10.62.7.0 network are 100, 0, and 10.62.7.78, respectively.
The metric and the next-hop address for the BGP routes can also be viewed by using the show ip route bgp command, as follows:
RouterA# show ip route bgp
B 10.62.7.0 [200/0] via 10.62.7.78, 01:34:16
B 200.17.56.0 [200/0] via 10.62.7.78, 01:34:16
B 192.177.1.0 [20/100] via 10.62.7.115, 01:34:16
The BGP table version can also be displayed by using the show ip bgp neighbors and the show ip bgp summary commands. The show ip bgp neighbors command also displays the address, ASN, and RID of neighbors of the local router, as shown below:
RouterA# show ip bgp neighbors
BGP neighbor is 192.177.1.6, remote AS 200, external link
BGP version 17, remote router ID 200.17.34.15
BGP state = Established, table version = 16, up for 01:45:03
The show ip bgp summary command displays the RID and the BGP table version, as shown in the following output:
RouterA# show ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 200.17.34.15, local AS number 100
BGP table version is 17, main routing table version 18
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.62.7.90 17 200 56 55 18 0 0 01:42:13 27
10.62.7.145 17 300 34 33 18 0 0 00:31:20 0
The router is not aware of the best path for the 61.80.3.0 route. The character h appears at the beginning of the entry for the 61.80.30 destination. This means that the route is in the history state currently and that the best route is not known.
There are not four AS between the router and the 192.177.1.0 subnet. In the output, the Path column for the 192.1771.1.0 subnet lists four AS numbers. The four AS numbers refer to the ASNs traversed by the route from RouterA to the
192.177.1.0 subnet. The first AS refers to the first neighbor of RouterA; the second AS refers to the neighbor of the first neighbor; and so on. The last AS in the column is the AS of the 192.177.1.0. This implies that there are three AS (1, 2, and 3) that exist between RouterA and the subnet.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify eBGP (IPv4 and IPv6 address families)
References:
Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference > show ip bgp Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference > show ip route bgp Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference > show ip bgp summary
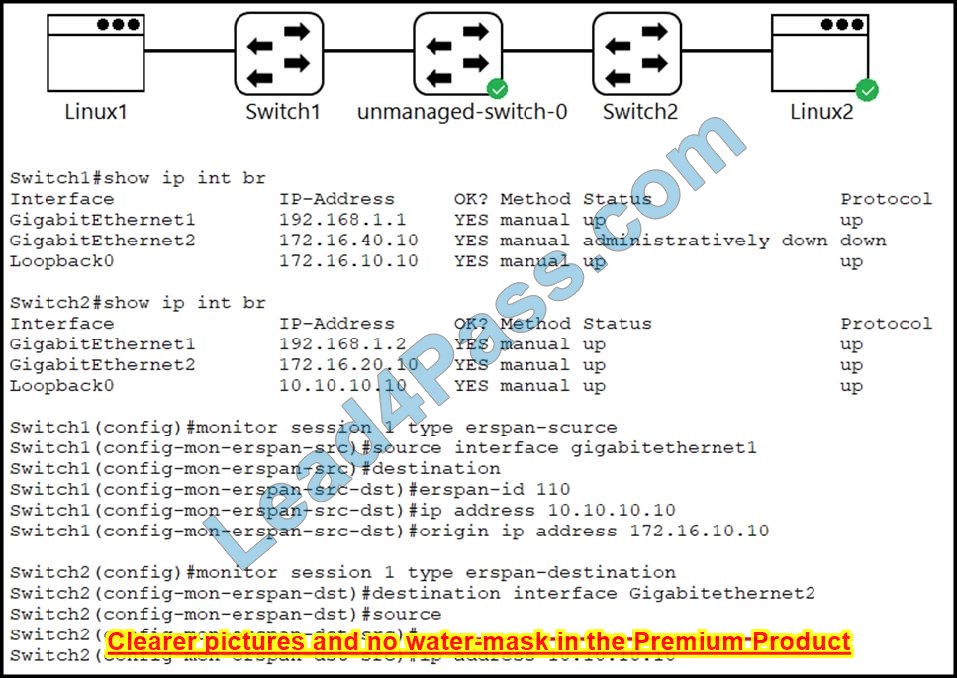
New Question 8:
Refer to the exhibit.
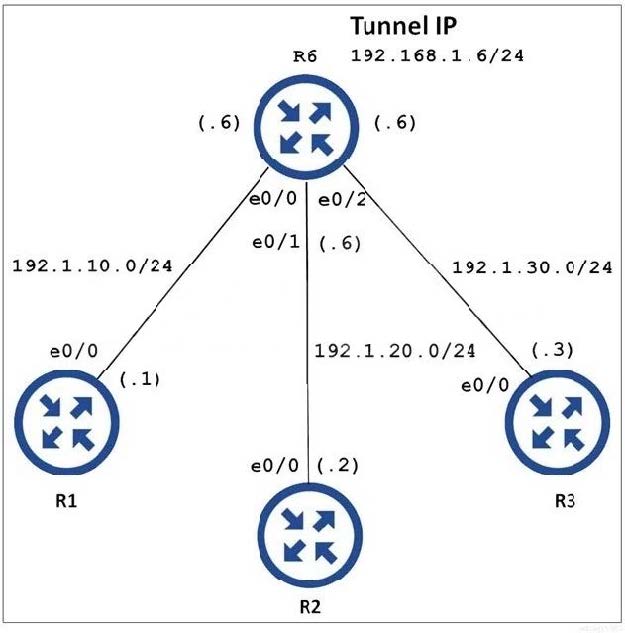
An engineer must establish multipoint GRE tunnels between hub router R6 and branch routers R1, R2, and R3. Which configuration accomplishes this task on R1?
A. interface Tunnel 1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 tunnel source e0/1 tunnel mode gre multipoint ip nhrp network-id 1 ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.6 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.6 192.1.10.1 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.2 192.1.20.2 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.3 192.1.30.3
B. interface Tunnel 1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 tunnel source e0/0 tunnel mode gre multipoint ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.6 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.6 192.1.10.1 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.2 192.1.20.2 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.3 192.1.30.3
C. interface Tunnel 1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 tunnel source e0/1 tunnel mode gre multipoint ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.6 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.6 192.1.10.6
D. interface Tunnel 1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
tunnel source e0/0
tunnel mode gre multipoint
ip nhrp network-id 1
ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.6
ip nhrp map 192.168.1.6 192.1.10.6
Correct Answer: D
We have an example of how to configure DMVPN Phase II and we show the configuration here for your reference:

Diagram DMVPN Phase II ?Dynamic Mapping

Text
Note: Although Phase II Dynamic Mapping is “dynamic” but we still need to add a static entry for the hub because without that entry, the NHRP registration cannot be sent.
New Question 9:
Examine the following diagram:

Which of the following actions will make area 1 a totally stubby area? (Choose all that apply. Each correct answer is part of the solution.)
A. execute the area 1 stub no-summary command on RouterA
B. execute the area 1 stub no-summary command on RouterB
C. execute the area 1 stub command on RouterB
D. execute the area 1 stub command on RouterA
E. execute the area 0 stub-no summary command on RouterA
F. execute the area 0 stub no-summary command on RouterB
G. execute the area 0 stub command on RouterB
H. execute the area 0 stub command on RouterA
Correct Answer: AC
You should execute the area 1 stub no-summary command on RouterA and the area 1 stub command on RouterB. A totally stubby area is one that only keeps local area routes in the link-state database (LSDB), plus a default route that leads out of the area.
To make an area totally stubby, the area border router (ABR) should be configured with the area 1 stub no-summary command and all other area routers should be configured with the area 1 stub command. The diagram in the scenario indicates that RouterA is the border router. You should not run any of the commands that refer to area 0. This would affect a different area than the requirement stated in the scenario.
None of the other combinations of actions will create a totally stubby area.
If you run the area 1 stub command on both RouterA and RouterB, it will create a stub area. A stub area differs from a totally stubby area in that a stub area will allow updates about areas in the same OSPF domain.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify network types, area types, and router types
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > What Are OSPF Areas and Virtual Links? > Define a Totally Stub Area
New Question 10:
Which show command displays entries in a router\’s Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) table?
A. show ip bgp
B. show ip bgp table
C. show ip bgp topology
D. show ip bgp summary
Correct Answer: A
The correct command is show ip bgp.
The BGP table lists all the paths that the BGP router has learned. Each destination network listed might have multiple possible paths listed. Given that the criteria are met for each destination network, BGP will choose a path to put in the IP routing table.
The BGP table is in many ways analogous to EIGRP\’s topology table in that it lists many known paths, not just the best path. Below is an example partial output of the show ip bgp command:

The following facts can be determined from this output:
All of the routes were redistributed into BGP from an IGP. In the status column (located to the left of the Network column and to right of the column where some lines have a > symbol) is a column that is either blank or has an i symbol.
In this case, all of the columns are blank. If the status column is blank, then BGP learned the route from an external peer. If it has an i symbol, an iBGP neighbor advertised this path to the router. It was learned from an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) and was advertised as a result of executing a network statement on the neighbor under the router bgp context as shown below adding the 30.0.0.0 network under BGP 100.
R4(config)#router bgp 100
R4(config-router)#network 30.0.0.0
Four routes will be installed in the routing table. These routes have both an * symbol and a > symbol. l in the status column. The * symbol indicates that the next hop is valid and the > symbol indicates that this is the best route.
The output is slightly different if you specify the network that you are interested in, as shown below in the show ip bgp 214.5.98.0 command output:

This output focuses solely on the route to the network 214.5.98.0 and provides the following pieces of information:
The neighbor that sent this route is at 192.168.1.1
The AS of the network where 214.5.98.0 is located is 5760
The IGP metric to reach the neighbor that sent this route is 886, as shown by the text 192.168.1.1 (metric 886) The complete metric to 214.5.98.0 is 1652, as shown in the last line by Origin IGP, metric 1652
The commands show ip bgp table and show ip bgp topology are not valid Cisco commands.
The show ip bgp summary command displays the status of BGP connections.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Explain BGP attributes and best-path selection
References:
Cisco IOS Master Command List, Release 12.4 > l through q > Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference > show ip bgp
New Question 11:
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer notices a connectivity problem between routers R1 and R2. The frequency of this problem is high during peak business hours. Which action resolves the issue?
A. Increase the available bandwidth between R1 and R2.
B. Decrease the EIGRP keepalive and hold down timers on R1 and R2.
C. Increase the MTU on the interfaces that connect R1 and R2.
D. Set static EIGRP neighborship between R1 and R2.
Correct Answer: A
EIGRP DUAL-3-SIA
1.
Missing or incorrect bandwidth interface configuration parameter
2.
Incorrect bandwidth configured to influence path selection https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/enhanced-interior-gateway-routing-protocol-eigrp/13676-18.html
New Question 12:
Refer to the exhibit The enterprise users fail to authenticate with the TACACS server when a direct fiber link fails between RB and RD The NOC team observes Users connected on AS65201 fail to authenticate with TACACS server 192 168 1 Users connected on AS65101 successfully authenticate with TACACS server 192 168 1 1 All AS65101 and AS65201 users are configured to authenticate with the TACACS server Which configuration resolves the issue?


A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: C
New Question 13:
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer executes the show ipv6 ospf database command and is presented with the output that is shown. Which flooding scope is referenced in the link-state type?
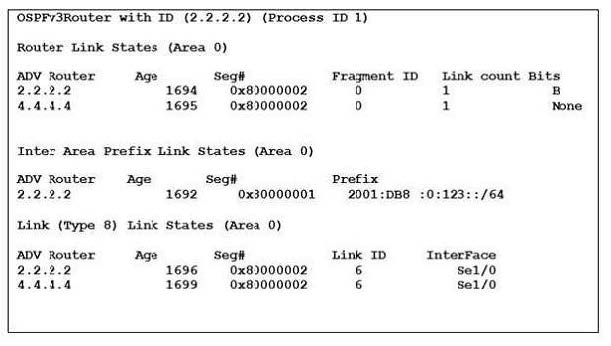
A. link-local
B. area
C. As (OSPF domain)
D. reserved
Correct Answer: B
New Question 14:
Refer to the exhibit.

The administrator configured route advertisement to a remote low resources rooter to use only the default route to reach any network but failed. Which action resolves this issue?
A. Change the direction of the distribute-list command from out to in.
B. Remove the line with the sequence number 5 from the prefix list.
C. Remove the prefix keyword from the distribute-list command.
D. Remove the line with the sequence number 10 from the prefix list.
Correct Answer: B
New Question 15:
Refer to the following exhibit, where three routers have EIGRP for IPv6 enabled on them:
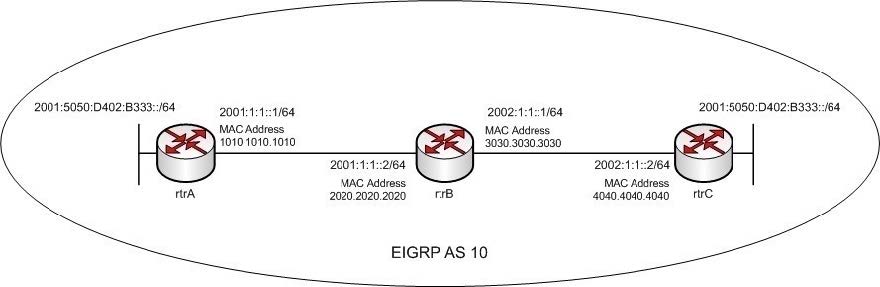
What is the next-hop address when rtrB advertises the 2001:5050:D402:B333::/64 IPv6 subnet to rtrC?
A. FE80::3030:3030:3030/64
B. FE80::3230:3030:3030/64
C. FE80::3030:30FF:FE30:3030/64
D. FE80::3230:30FF:FE30:3030/64
Correct Answer: D
The next-hop address when rtrB advertises the 2001:5050:D402:B333::/64 IPv6 subnet to rtrC is FE80::3230:30FF:FE30:3030/64. In routers with EIGRP for IPv6 enabled on them, the next-hop address is the IP address of the interface that advertises routes. The next-hop addresses should be link-local addresses. Link-local addresses are IPv6 unicast addresses that are automatically assigned to the router interfaces. These addresses have the FE80::/10 prefix and the EUI-64 standard interface address.
EUI-64 is an IEEE standard that allows the determination of an IPv6 address from the MAC address of an interface. The 64 most significant bits should be specified in the ipv6 address command. The 64 least significant bits are determined by using the EUI-64 standard. The steps to determine the 64 least significant bits are as follows:
1.
Divide the 48-bit MAC address into two 24-bit parts.
2.
Embed FFFE (16 bits) between the two parts resulting in a 64-bit address.
3.
If required, toggle the seventh bit of the first octet in the address. In EUI-64 format, if the seventh bit is 0, then the address is local. If the seventh bit is 1, the address is global.
In this case, when rtrB advertises any route to rtrC, it advertises the interface with the MAC address 3030.3030.3030 as the next-hop. When the given steps are performed on the MAC address, it result in the EUI-64 standard address
3230.30FF.FE30:3030. This address is then appended to the FE80::/10 prefix. The resultant IPv6 link-local address of the interface is FE80::3230.30FF.FE30:3030/10.
The remaining three options are incorrect as their interface address is not in the EUI-64 standard.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Identify IPv6 addressing and subnetting
References:
Cisco IPv6 Configuration Guide, Release 15.2 > IPv6 Neighbor Redirect Message Cisco IPv6 Configuration Guide, Release 15.2 > IPv6 Unicast Routing > Aggregatable Global Address
| Download New Leads4Pass 300-410 Exam Materials: | 300-410 PDF Download |
Final conclusion
It is very important that the 300-410 ENARSI certification exam materials are updated to ensure that they are valid in real time and the Leads4pass 300-410 dumps are always updated! And provide all members with 365 days of free use!
Use Cisco 300-410 Dumps exam material, 3-day practice plan! Ensure you have 100% success in passing the CCNP Enterprise 300-410 exam.
FAQs
Will Cisco 300-410 ENARSI certification still be popular in 2025?
Cisco 300-410 ENARSI certification will still be in high demand in 2025: 1. The certification still has strong market demand, especially in the fields of advanced routing protocols, VPN technology and other network technologies. 2. ENARSI certification will increase with It will continue to evolve over time, but the core networking principles and skills it assesses remain extremely valuable to networking professionals.
Will the Cisco 300-410 ENARSI exam be updated?
All updates from last year to the end of the year have ended. However, as time goes by and technology develops, it is likely that there will be further updates. Pay attention to official news and get the latest developments in real time.
Cisco 300-410 ENARSI certification salary level in 2025?
The Cisco 300-410 ENARSI is a very valuable certification that really increases your earning potential. However, the actual improvement will be judged based on your work experience, work location, company size, and your own added value. The most critical point has to be said: this is the truth about the global market environment, and individual power cannot change it.